Composite
Definition
Compose objects into tree structures to represent part-whole hierarchies. Composite lets clients treat individual objects and compositions of objects uniformly.
Summary
The Composite pattern allows the creation of objects with properties that are primitive items or a collection of objects. Each item in the collection can hold other collections themselves, creating deeply nested structures.
A tree control is a perfect example of a Composite pattern. The nodes of the tree either contain an individual object (leaf node) or a group of objects (a subtree of nodes).
All nodes in the Composite pattern share a common set of properties and methods which supports individual objects as well as object collections. This common interface greatly facilitates the design and construction of recursive algorithms that iterate over each object in the Composite collection.
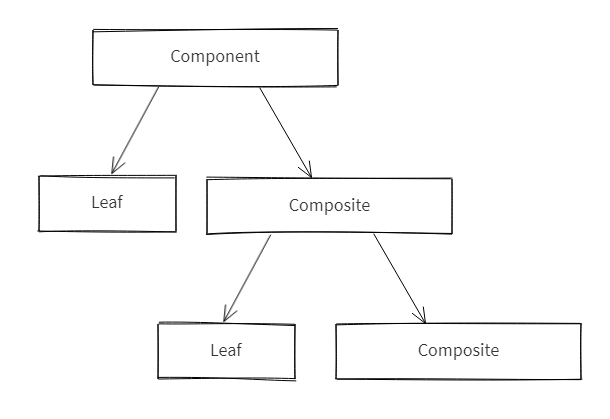
Participants
The objects participating in this pattern are:
Component -- in sample code: Node
- declares the interface for objects in the composition
Leaf -- in sample code: Node
- represent leaf objects in the composition. A leaf has no children
Composite -- in sample code: Node
represents branches (or sub trees) in the composition
maintains a collection if child
Sample code in JavaScript
In our example a tree structure is created from Node objects. Each node has a name and 4 methods: add, remove, getChild and hasChild. The methods are added to Node's prototype. This reducer the memory requirements as these methods are now shared by all now shared by all nodes. Node is fully recursive and there is no need for separate Component or Leaf objects.
A small Composite tree is built by adding nodes to parent nodes. Once complete we invoke traverse which iterates over each node in the tree and displays its name and depth (by showing indentation)
The log function is a helper which collects and displays results..
// Node
var Node = function(name) {
this.children = [];
this.name = name;
};
// Add Method
Node.prototype.add = function(child) {
this.children.push(child);
};
// Remove Method
Node.prototype.remove = function(child) {
var length = this.children.length;
for (var i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (this.children[i] === child) {
this.children.splice(i, 1);
return;
}
}
};
// Get Child Method
Node.prototype.getChild = function(i) {
return this.children[i];
};
// Has Child Method
Node.prototype.hasChiled = function() {
return this.children.length > 0;
};
// Recursively traverse a sub tree
function traverse(indent, node) {
var length = node.children.length;
log.add(Array(indent++).join('--') + node.name);
for (var i = 0; i < length; i++) {
traverse(indent, node.getChild(i));
}
};
// Log helper
var log = (function () {
var log = "";
return {
add: function (msg) { log += msg + "\n"; },
show: function () { console.log(log); log = ""; }
}
})();
// Client
function run() {
// Instance of Node
var tree = new Node('root'),
left = new Node('left'),
right = new Node('right'),
leftLeft = new Node('leftLeft'),
leftRight = new Node('leftRight'),
rightLeft = new Node('rightLeft'),
rightRight = new Node('rightRight');
tree.add(left);
tree.add(right);
tree.remove(right);
tree.add(right);
left.add(leftLeft);
left.add(leftRight);
right.add(rightLeft);
right.add(rightRight);
traverse(1, tree);
log.show();
};